
Saturday, 15 July 2006
150-12
The Water Quality Status of River and Groundwater in Fluvio-marine Deposit Area in Southeastern Korea.
Jeeyeon Ko, Jae-saeng Lee, Choon-song Kim, Ki-yeol Jung, Yeong-dae Choi, Eul-soo Yun, Choon-sik Kim, and Seong-tae Park. National Institute of Crop Science, Yeongnam Agricultural Research Institute, Neidong 1085, Milyang, South Korea
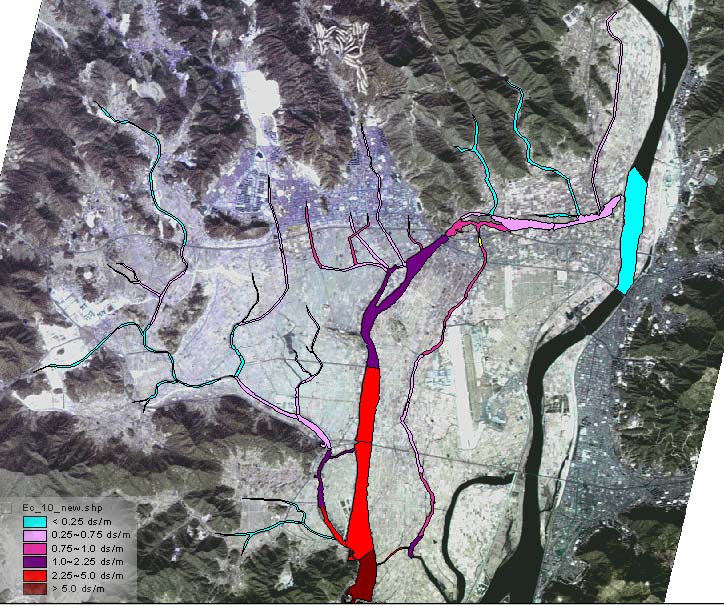
This study was conducted to evaluate the water quality distribution at fluvio-marine deposit area. The studied watershed, West-nackdong River, was located at Korea's southeastern part, which has complex pollution sources such as the city, intensive greenhouse agriculture, and rice paddy field areas and sea. For distinction of distribution status of river water and groundwater, the water components based on their nutrient material and marine were investigated and mapped by using GIS and satellite imaging. The T-N concentrations of river water were affected by urbanization in the northern part of watershed, all streams connected to the very urbanized Kimhae City, which exceeded 16 mg/µ¤. This was too high for agricultural use. Other nutrient components were similar with T-N. The marine components such as Cl, Na, and SO4 of river water were high at the southern part near the sea and the groundwater had a similar trend. When the watershed area was divided to some sectors, each sector's dominant pollution source and affected water quality status were different. Thus, suitable countermeasures for each sector were needed to improve water quality for agricultural purposes in complex pollution sources existing like in a fluvio-marine deposit area.
Back to 3.1B Translating Soil Science into Agricultural & Environmental Policy - Poster
Back to WCSS
Back to The 18th World Congress of Soil Science (July 9-15, 2006)